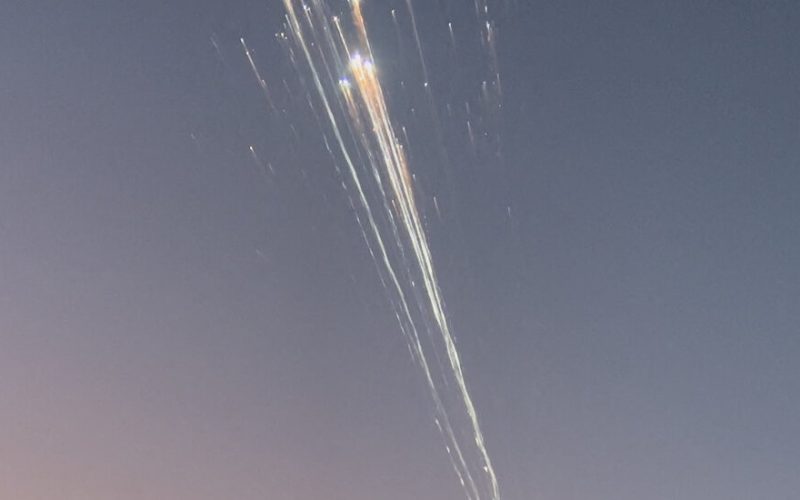
The urgent radio calls by the air traffic controllers at the Federal Aviation Administration office in Puerto Rico started to go out on Thursday evening as a SpaceX test flight exploded and debris began to rain toward the Caribbean.
Flights near Puerto Rico needed to avoid passing through the area — or risk being hit by falling chunks of the Starship, the newest and biggest of Elon Musk’s rockets.
“Space vehicle mishap,” an air traffic controller said over the F.A.A. radio system, as onlookers on islands below and even in some planes flying nearby saw bright streaks of light as parts of the spacecraft tumbled toward the ocean.
Added a second air traffic controller: “We have reports of debris outside of the protected areas so we’re currently going to have to hold you in this airspace.”
The mishap — the Starship spacecraft blew up as it was still climbing into space — led the F.A.A. on Friday to suspend any additional liftoffs by SpaceX’s Starship, the largest and most powerful rocket ever built.
The incident raises new questions about both the safety of the rapidly increasing number of commercial space launches, or at least the air traffic disruption being caused by them.
It also is the latest incident highlighting the conflicts that Elon Musk’s new role in the Trump administration will bring. He will have the remit to recommend changes, and potentially budget cuts, to government agencies including the F.A.A. That tension could hamper investigations like the one announced on Friday.
Mr. Musk, who is preparing to travel to Washington to participate in Mr. Trump’s inauguration, expressed confidence even as of Thursday night that SpaceX would resolve questions about the explosion quickly and restart test flights.
“Nothing so far suggests pushing next launch past next month,” Mr. Musk wrote on his social media site, X.
Mr. Musk also made fun of the spectacle the explosion created, as the debris fell toward Turks and Caicos Islands. “Success is uncertain, but entertainment is guaranteed!” atop a video of the fiery debris falling toward earth.
The explosion happened after the Starship’s second stage — which is slated to carry cargo or even astronauts on their way to the moon during future missions — separated from the lower Super Heavy booster, and was flying at about 13,250 miles per hour, 90 miles above the Earth.
The Starship had already fired its own rockets to finish the trip into orbit, according to SpaceX’s ship tracking information, suggesting that at the time it blew up, it weighed somewhat more than 100 tons, which is the Starship’s approximate mass without fuel.
SpaceX and F.A.A. officials on Friday did not respond to questions submitted in writing and in interviews by The New York Times as to whether the explosion and falling debris may have represented a threat to any aircraft or people on the ground. It is unclear how much of the spacecraft might have burned up as it fell.
The agency did say there were no reports of injuries but is investigating reports of property damage on Turks and Caicos. It also said that several aircraft that were asked to hold in an area away from the falling debris ended up having to divert and return to other airports because of low fuel.
SpaceX, in a statement about this seventh Starship test flight, said that early data suggested that a fire had started in the rear section of the spacecraft, resulting in the explosion and the landing of debris in an area that SpaceX and the F.A.A. had already identified as liable to such hazards.
Closer to the South Texas launch site, at the edge of the Gulf of Mexico, all flights were already banned at the time of the launch. Starship was about 10 times higher than the altitude of commercial flights when it exploded, meaning there should have been time to warn any planes in the area to steer clear before any remaining debris approached.
SpaceX will be in charge of the mishap investigation, but it will be overseen by the F.A.A., which could allow it to resume test flights even before the investigation is complete, if SpaceX can document that the accident did not create a safety hazard.
Mr. Musk has previously expressed frustration at how long it takes the agency to approve Starship launch licenses. Now he will be a prominent member of the Trump administration, through his perch as a co-leader of an advisory group called the Department of Government Efficiency, with the power to evaluate federal spending and regulations.
“What this new administration might do is push this review to its conclusion faster,” said Todd Harrison, a former space industry executive at America Enterprise Institute.
He added that he expected some at F.A.A. might want to put new demands on SpaceX related to what time future Starship test flights launch, or broader restrictions on flights along more of the flight path.
Tim Farrar, a satellite industry consultant, said the incident showed the complications the United States is going to face as it ramps up space launches, both for the Pentagon as it builds out space warfighting capacity, and major commercial companies like SpaceX and Amazon that are building constellations with thousands of satellites to create global broadband internet access from orbit.
“How much can you realistically increase the tempo of these launches?” Mr. Farrar said.
There were 145 launches reaching orbit last year from the United States, compared with just 21 five years ago. An extraordinary 133 of those orbital launches were by SpaceX, which is now the world’s dominant space company, according to data collected by Jonathan McDowell, an astrophysicist who tracks launches globally.
Most of those SpaceX launches were by the Falcon 9 rocket, which is deploying Starlink communications satellites and Pentagon payloads and was not impacted by Friday’s F.A.A. order.
Blue Origin, the launch company created by Jeff Bezos, had its own rocket test on Thursday, reaching orbit for the first time with its spacecraft called New Glenn. But it launched from Cape Canaveral in Florida at 2:03 a.m., in part because there were fewer planes in the air then.
The surge in launch frequency, even before Thursday, has been generating complaints from airlines, including Qantas, the Australian-based carrier, which told reporters this month that it has had to delay several flights between Johannesburg and Sydney at the last minute because of debris from SpaceX Falcon 9 rockets.
“While we try to make any changes to our schedule in advance, the timing of recent launches have moved around at late notice which has meant we’ve had to delay some flights just prior to departure,” the Qantas executive said in a statement.
Hannah Walden, an Airlines for America spokeswoman, said the commercial airlines are tracking this issue closely.
“Safety is the top priority for U.S. airlines, and we are committed to ensuring the safety of all flights amidst the growing number of space launches,” she said in a statement. “We continuously collaborate and coordinate with the federal government and commercial space stakeholders to ensure the U.S. airspace remains safe for all users.”
Bill Nelson, the Biden-era National Aeronautics and Space Administration director, praised the test flight. The space agency has more than $4 billion worth of contracts with SpaceX to twice use Starship to land astronauts on the moon.
“Spaceflight is not easy,” he wrote Thursday night on Mr. Musk’s X platform. “It’s anything but routine. That’s why these tests are so important — each one bringing us closer on our path to the Moon and onward to Mars.”
Mark Walker contributed reporting.